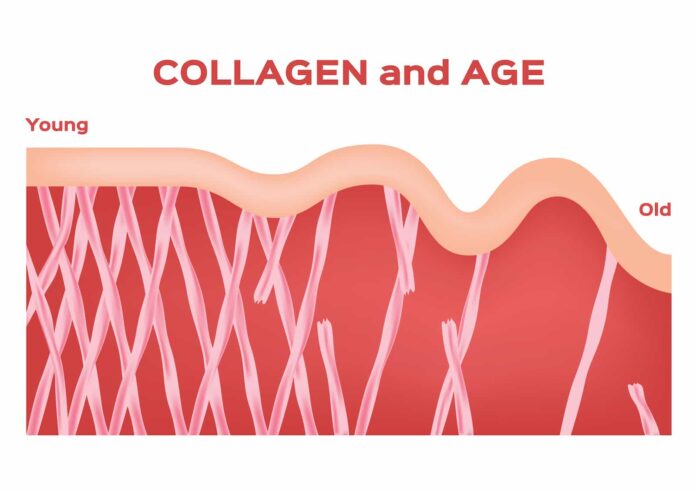
Collagen becomes more important for the body after the age of 30 for several reasons related to its critical role in maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of various tissues. Here are the key points:
- Natural Decline in Production:
- After the age of 30, the body’s natural collagen production starts to decline at a rate of about 1-2% per year. This reduction in collagen synthesis leads to a gradual loss of structural support in tissues.
- Skin Health:
- Collagen is a major component of the skin, providing strength and elasticity. As collagen production decreases, the skin can become thinner, less elastic, and more prone to wrinkles and sagging. Maintaining collagen levels can help slow these signs of aging.
- Joint Health:
- Collagen is a key component of cartilage, which cushions joints. With age, reduced collagen can contribute to the breakdown of cartilage, leading to joint pain and conditions like osteoarthritis. Supporting collagen production can help maintain joint health and mobility.
- Bone Density:
- Collagen provides a structural framework for bones. Decreased collagen can lead to a reduction in bone density, increasing the risk of fractures and conditions such as osteoporosis. Ensuring adequate collagen levels can help preserve bone strength.
- Tendon and Ligament Integrity:
- Collagen is vital for the strength and flexibility of tendons and ligaments. A decline in collagen can result in weaker connective tissues, increasing the risk of injuries and reducing overall physical performance.
- Overall Tissue Repair:
- Collagen plays a role in the repair and regeneration of various tissues. As the body’s ability to produce collagen diminishes, the efficiency of tissue repair processes also declines. Supporting collagen synthesis can aid in maintaining tissue health and recovery from injuries.
Given these points, maintaining adequate collagen levels through diet, supplements, and lifestyle choices can help mitigate the effects of aging and support overall health and well-being.