Chickenpox: Symptoms and Treatment
Chickenpox is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It primarily affects children but can occur in adults. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Symptoms of Chickenpox
Chickenpox symptoms appear 10–21 days after exposure to the virus and typically include:
- Fever: Low-grade fever often appears first.
- Fatigue and Weakness: A feeling of general discomfort or tiredness.
- Loss of Appetite: Decreased desire to eat.
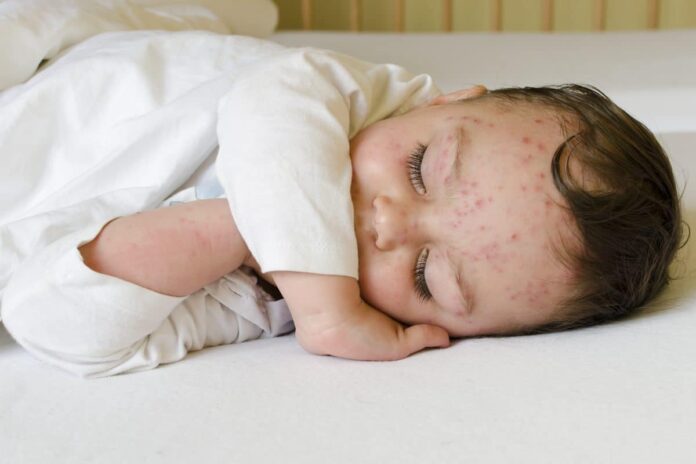
- Rash Development:
- Stages:
- Red Spots: Flat, red spots appear on the skin.
- Blisters: These spots turn into fluid-filled blisters (vesicles).
- Scabs: Blisters eventually dry out and form scabs.
- Rash usually starts on the face, chest, or back and then spreads to the rest of the body, including the scalp, mouth, and genitals.
- The rash can be intensely itchy.
- Stages:
- Other Symptoms (less common):
- Headache
- Sore throat
- Irritability in young children
Complications (Rare but Possible)
- Bacterial skin infections
- Pneumonia
- Brain inflammation (encephalitis)
- Reye’s syndrome (associated with aspirin use in children)
- More severe complications in immunocompromised individuals or pregnant women.
Treatment and Management
1. General Care
- Rest: Ensure the patient gets plenty of rest.
- Hydration: Drink lots of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Avoid Scratching: Scratching the rash can cause infections and scarring. Keep nails short.
2. Medications
- Antiviral Drugs:
- Acyclovir: May be prescribed, especially for adults, pregnant women, or immunocompromised patients.
- Antihistamines:
- To relieve itching (e.g., diphenhydramine).
- Pain and Fever Relief:
- Use acetaminophen (paracetamol) for fever and pain. Avoid aspirin due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome.
3. Soothing the Rash
- Calamine Lotion: Apply to soothe itchy skin.
- Cool Compresses: Use cool, damp cloths to relieve irritation.
- Oatmeal Baths: Add colloidal oatmeal to bathwater for relief.
4. Isolation
- Avoid contact with others (especially pregnant women and those not immune to chickenpox) until all blisters have scabbed over, which usually takes about a week.
Prevention
- Vaccination:
- Varicella Vaccine: Provides immunity and significantly reduces the risk of severe chickenpox.
- Recommended in two doses:
- First dose: 12–15 months of age.
- Second dose: 4–6 years of age.
- Adults who haven’t had chickenpox or been vaccinated should get the vaccine.
- Exposure Control:
- Isolate infected individuals during the contagious period.
- Practice good hygiene, including frequent handwashing.
When to See a Doctor
- If the rash spreads to the eyes.
- High fever persists for more than 4 days.
- Severe itching that cannot be controlled.
- Signs of infection like redness, swelling, or oozing from blisters.
- Breathing difficulties or confusion.
Would you like tips on how to manage the discomfort at home or details about the vaccination schedule?