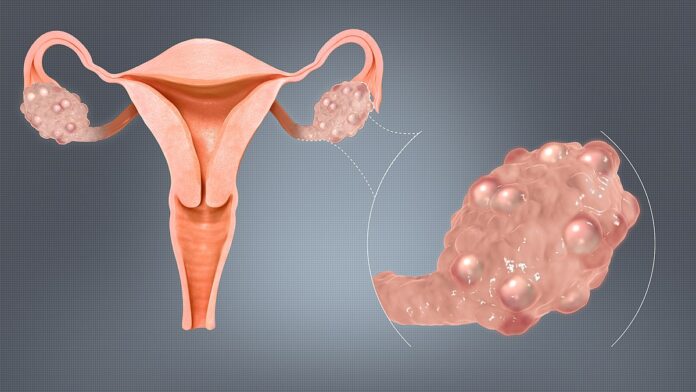
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting women of reproductive age. The symptoms and management strategies can vary, but here are some key points often suggested by experts for recognizing and managing PCOS:
Symptoms of PCOS
- Irregular Periods: This can include fewer menstrual cycles (fewer than eight in a year), prolonged periods, or even a complete absence of menstruation.
- Excess Androgen: High levels of male hormones can lead to physical signs such as excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), severe acne, and male-pattern baldness.
- Polycystic Ovaries: Enlarged ovaries containing numerous small cysts can be detected via ultrasound.
- Weight Gain: Many women with PCOS struggle with weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
- Insulin Resistance: This can lead to higher levels of insulin in the body, contributing to weight gain and increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Thinning Hair: Hair on the scalp may become thinner.
- Skin Issues: Skin may become oilier and more prone to acne and dark patches (acanthosis nigricans) may appear, especially around the neck and underarms.
Management Methods
- Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: Adopt a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Reducing processed foods and sugars can help manage weight and insulin levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help reduce insulin resistance, maintain a healthy weight, and alleviate some PCOS symptoms. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Weight Management: Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of body weight can improve symptoms and regulate menstrual cycles.
- Medications
- Hormonal Birth Control: Oral contraceptives can regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and improve acne and hirsutism.
- Metformin: Often prescribed to manage insulin resistance and lower insulin levels.
- Anti-Androgens: Medications such as spironolactone can reduce androgen levels and improve symptoms like hirsutism and acne.
- Clomiphene: For women trying to conceive, this medication can stimulate ovulation.
- Supplements
- Inositol: A supplement that can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate menstrual cycles.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: May help reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Vitamin D: Many women with PCOS are deficient in vitamin D; supplementation may improve symptoms.
- Alternative Therapies
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest acupuncture may help improve ovulation and reduce symptoms.
- Herbal Remedies: Certain herbs like spearmint tea, cinnamon, and licorice root are believed to have beneficial effects on PCOS symptoms, though more research is needed.
- Stress Management
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress, which can exacerbate symptoms.
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensuring adequate and quality sleep is crucial as poor sleep can worsen insulin resistance and hormonal imbalance.
Regular Monitoring and Medical Advice
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as necessary. Blood tests to monitor hormone levels, blood sugar, and cholesterol are often part of routine management.
Conclusion
While PCOS can be challenging to manage, a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and alternative therapies can significantly improve symptoms and overall quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen.