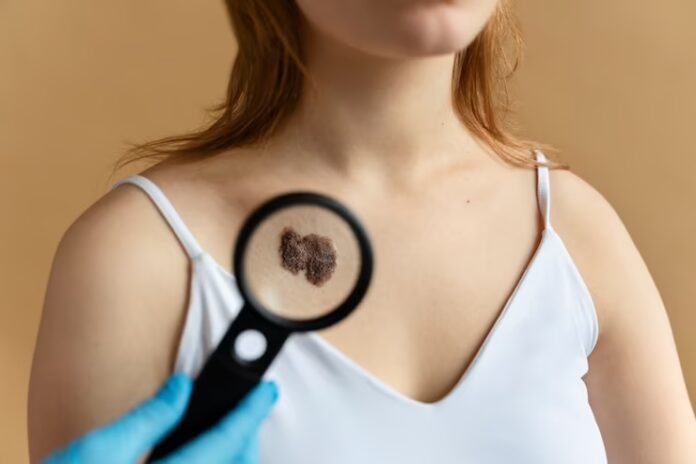
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer and occurs when abnormal cells in the skin grow and divide uncontrollably, forming a tumor. The majority of skin cancers are caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Skin cancer can be divided into three major types: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. In this article, we will discuss each of these types in detail.
Basal Cell Carcinoma: Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer and is usually caused by exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds. It typically appears as a small, shiny bump or a red, scaly patch that does not heal. This type of cancer grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body. However, if left untreated, it can cause significant damage to the surrounding tissue and lead to disfigurement.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer and is also caused by exposure to UV radiation. It typically appears as a firm, red bump or a scaly patch on the skin. It can grow quickly and may spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Squamous cell carcinoma can also be caused by long-term exposure to certain chemicals or radiation.
Melanoma: Melanoma is a less common but more dangerous type of skin cancer. It can develop anywhere on the body, including areas that are not exposed to the sun. Melanoma usually appears as a mole or a dark spot on the skin. It can grow quickly and spread to other parts of the body, making it much more difficult to treat. Melanoma is responsible for most skin cancer-related deaths.
Risk Factors: Anyone can develop skin cancer, but certain factors increase the risk. These include fair skin, a history of sunburns, a family history of skin cancer, exposure to UV radiation, a weakened immune system, and certain genetic disorders.
Prevention: The best way to prevent skin cancer is to protect your skin from UV radiation. This can be done by staying out of the sun during peak hours (10 am-4 pm), wearing protective clothing such as hats and long sleeves, and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. It is also important to avoid tanning beds, which are a major source of UV radiation.
Treatment: Treatment for skin cancer depends on the type and stage of cancer. Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are usually treated with surgery, while melanoma may also require chemotherapy or radiation therapy. In some cases, targeted therapy or immunotherapy may be used to treat melanoma.
Conclusion: Skin cancer is a serious and potentially deadly disease that can be prevented by taking simple steps to protect your skin from UV radiation. If you notice any unusual spots or moles on your skin, it is important to see a dermatologist for evaluation. Early detection and treatment are key to a successful outcome.