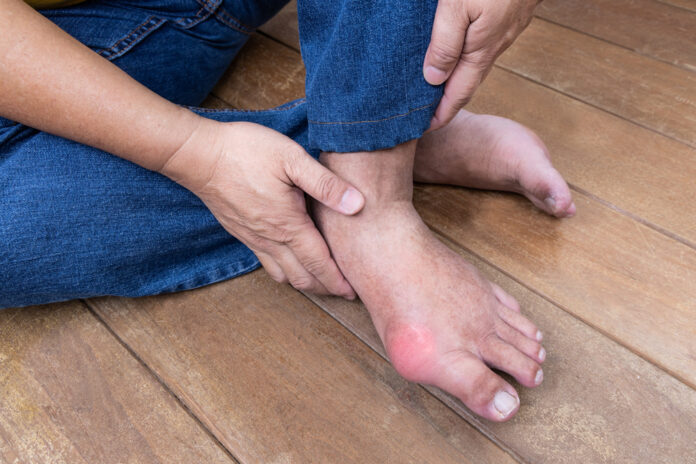
Uric acid is a chemical compound that is naturally produced in the human body as a result of the breakdown of purines, which are compounds found in certain foods and also formed by the body’s cells during metabolism. Uric acid is primarily excreted through the kidneys in urine, but when its levels become too high, it can lead to a medical condition known as hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia can, in turn, lead to health problems, most notably gout and kidney stones.
Here are some key aspects of uric acid:
- Role in the Body: Uric acid serves as an antioxidant and helps eliminate free radicals from the body. In small amounts, it is beneficial for the body’s overall health.
- Sources: Uric acid comes from two main sources:
- Endogenous Production: The body generates uric acid when it breaks down purines from cell turnover and metabolic processes.
- Exogenous Sources: Dietary purines are found in certain foods, such as red meat, seafood, and high-fructose corn syrup. When you consume these purine-rich foods, they can contribute to increased uric acid levels.
- Hyperuricemia: When there is an excessive accumulation of uric acid in the bloodstream, it can lead to hyperuricemia. This condition can result from overproduction of uric acid, underexcretion of uric acid, or a combination of both.
- Health Implications:
- Gout: Elevated uric acid levels can cause the formation of urate crystals, which can accumulate in joints, leading to a painful condition called gout. Gout is characterized by sudden and severe joint pain, often affecting the big toe.
- Kidney Stones: Uric acid can also form crystals in the urinary tract, leading to the development of kidney stones. These stones can cause pain and may require medical intervention to remove.
- Association with Other Conditions: High uric acid levels have been linked to an increased risk of other health conditions, such as hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease.
- Diagnosis: Hyperuricemia is typically diagnosed through a blood test, which measures the concentration of uric acid in the bloodstream.
- Treatment and Management:
- Dietary Changes: Dietary modifications can help manage uric acid levels. This may involve reducing the consumption of purine-rich foods and increasing the intake of fluids.
- Medications: In cases where hyperuricemia leads to gout or recurrent kidney stones, medications may be prescribed to lower uric acid levels or prevent crystal formation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and maintaining a healthy body weight, can also help manage uric acid levels.
- Prevention: To prevent hyperuricemia and its associated conditions, individuals can make dietary and lifestyle choices to manage uric acid levels, stay hydrated, and maintain a balanced diet.
It’s important to note that not everyone with high uric acid levels will develop gout or kidney stones. The relationship between uric acid and these conditions can be influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and other factors. If you have concerns about your uric acid levels or related health issues, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on management and treatment.